Technology & Facilities
BIPLANE CATH LAB
Biplane cath lab technology employs two X-ray sources and detectors to capture
simultaneous images of the heart from different angles. This enhances both precision
and safety during cardiac procedures. Biplane cath lab technology produces high-
resolution images of the heart and its vessels, making it easier for doctors to identify
and diagnose issues accurately.
Biplane cath lab technology used in Coronary Angiography , Percutaneous Coronary
Intervention (PCI), Valvuloplasty, Ablation, Closure of Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) and
Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO).
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY (OCT)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is an imaging modality that uses near-infrared light to
provide high-definition images of the artery with high precision allowing to access lesion
characteristics and plaque morphology for coronary artery disease. OCT provides
automated, accurate measurements to help guide stent selection, placement, and
deployment
EXTRACORPOREAL MEMBRANE OXYGENATION (ECMO)
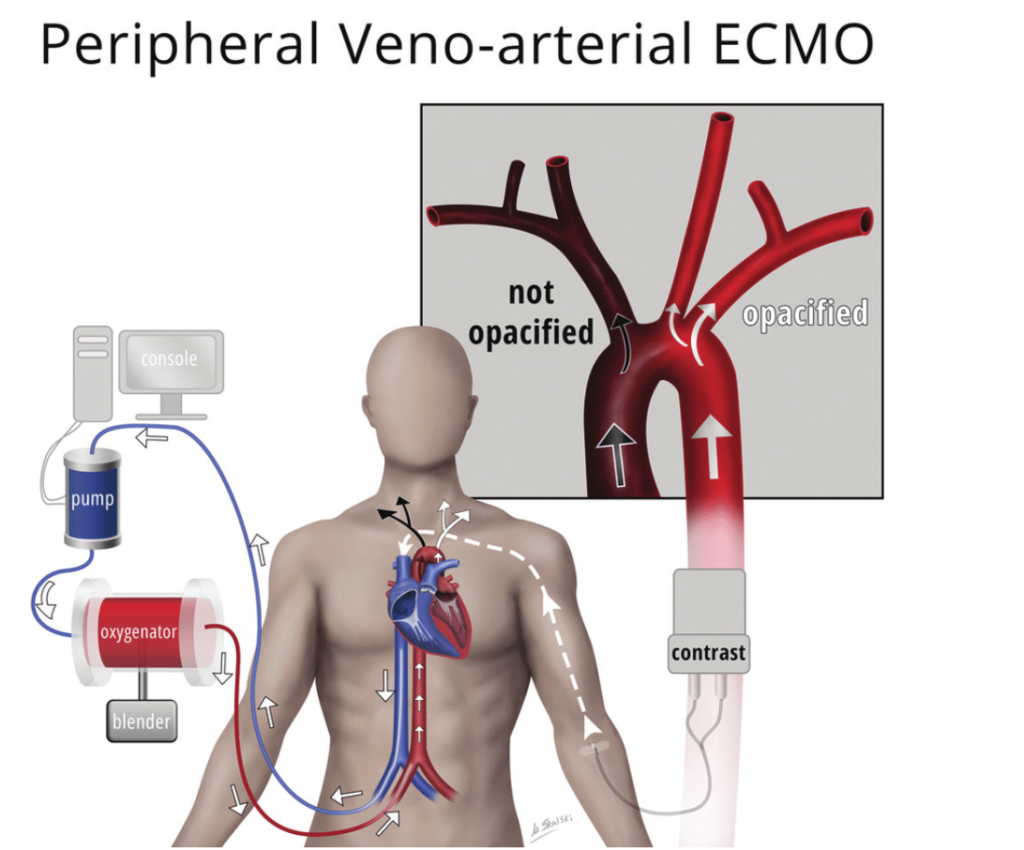
ECMO is a life support technique that provides both cardiac and respiratory support to
individuals whose heart and lungs are unable to provide adequate oxygenation and carbon
dioxide removal for the body. ECMO is typically used in critical situations, such as severe
respiratory failure or cardiac failure, where conventional treatments are insufficient. It
allows the heart and lungs to rest and recover by temporarily taking over their functions.
ECMO can be used in various settings, including neonatal intensive care units, paediatric
intensive care units, and adult intensive care units.
IMPELLA
IMPELLA, the world’s smallest heart pump is the only non-surgical heart pump FDA-
approved for patients undergoing high-risk PCI and those with cardiogenic shock.
Impella Heart Recovery Program, which was launched in several hospitals in India with the
goal of recovery of native heart, has saved many lives worldwide in sub-group of patients
undergoing Protected PCI & AMI -Cardiogenic Shock, Myocarditis, Cardiomyopathy, and
Post Cardiotomy Cardiogenic Shock.
It has also enabled patients who are waiting for a Heart Transplant to survive till they get a donor Heart.
The Impella Ventricular Support System acts as a blood pump that effectively bypasses the
left ventricle, it supports blood pressure and provides increased blood flow to critical organs
in patients with cardiogenic shock. This allows the left ventricle to rest and hopefully
recover and resume pumping without support. Clinical evidence demonstrated that 58% of
patients with cardiogenic shock who received the Impella device survived the procedure,
and 67% of patients who left the hospital experienced myocardial recovery (they did not
have another heart failure event) within 30 days of the procedure.
INTRAVASCULAR ULTRASOUND (IVUS)
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) is a diagnostic test. This test uses sound waves to see inside
blood vessels. It is useful for evaluating the coronary arteries that supply the heart.
FRACTIONAL FLOW RESERVE (FFR)
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is a technique used in coronary angiography to measure
pressure differences across a coronary artery stenosis (blockage) to determine the
likelihood that the stenosis impedes oxygen delivery to the heart muscle and thereby assess
whether to open it or not.
ORBITAL ATHERECTOMY
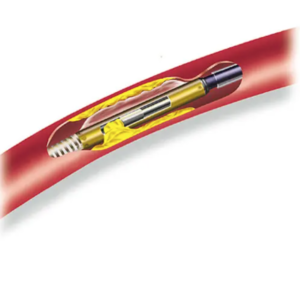
Orbital atherectomy (OA) is an adjunctive therapy used for lesion preparation of calcified plaque with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and peripheral percutaneous endovascular interventions. The goal of lesion preparation with OA is to modify calcified plaque, changing lesion compliance to allow adequate balloon and stent expansion in segments with heavily calcified lesions. This activity highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and improving care for patients undergoing this procedure.
Objectives:
- Describe the pathophysiology of coronary artery calcification.
- Outline the indications for orbital atherectomy.
- Identify the common complications of orbital atherectomy
- Describe the procedural technique for performing orbital atherectomy.